A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is an important but often overlooked part of web design and SEO. This guide will help you understand how to go about creating SEO-friendly URLs and how to avoid some common mistakes.
What is a URL? And is it important for SEO?
The URL of a particular website or page is its unique address that will show users how to find that page/website. It is the text that users will see in the address bar when browsing through your website.
Web addresses may not seem very important, but Google considers them a minor ranking factor. Google cares about a website’s user experience and, for this reason, the URL is one of the factors considered when judging a website. Google has even dedicated an entire page to them in their SEO advanced guide.
SEO best practices for URLs
You should do everything you can to make your website easy to browse for your users and Google’s web crawlers, which is why a well-optimized web address is so important.
Below are some important questions you should ask when building your URL structure:
What is the best URL structure for SEO?
Keeping the URL structure as simple as possible should be your focus when designing your web address. Make sure a user can easily read your address out loud if you are having trouble figuring out how a simple slug structure is supposed to look.
The goal of keeping the structure simple is to make it easier for the user to understand how your website is structured and how they can navigate it. Simplifying navigation is an excellent way to enhance user experience, which in turn improves how Google judges the quality of your website.
Below are some examples of well-structured URLs for different situations:
- Article/blog post: example.com/blog/blog-title
- Category page: example.com/category-name
- Product page: example.com/category-name/product-name
- Company about page: example.com/about-us
Should keywords be added to the URL?
Yes! Make sure to add keywords to your web address because this helps both users and Google’s bots understand the content on your website. Never add more than 1-2 keywords to the slug and make sure those keywords also describe the content on the page. As with most SEO best practices, it is essential to design for human users instead of robots.
When choosing the keywords to add to your web address, ensure they are your most important keywords. Using these keywords improves your rankings and may also help your click-through rate (CTR) on Google’s search page since web addresses are displayed along with your page title and description, as shown below.
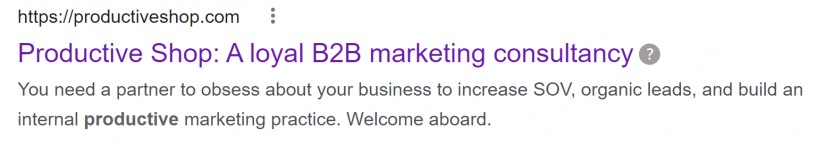
Having a clean and relevant URL show up in search is a great way to boost CTR.
How long should a URL be?
The maximum length of a URL is technically 2000 characters since browsers can’t display more characters than that. However, the ideal length is below 74 characters since Google only shows your address in search results if it is short and digestible. It is important to remember that overly long web addresses are difficult for users to understand and navigate and shorter URLs are easier to remember.
Should symbols be added to the URL?
A very small list of characters is allowed in a standard slug. You should stick to this list when designing your web address, as it could cause display issues in different systems and formats. You should avoid symbols such as exclamation marks, underscores and question marks in URLs.
You should note that some symbols have separate functions; for example, pound signs in URLs will point the user towards a particular part of a page.
Below is the list of acceptable characters:
– . + ! * ‘ ( ) , $
Should URLs include capital letters?
You should not add capital letters in URLs since they make it harder for users to read them. Although capital letters in URLs are allowed, it is a widely recognized best practice to avoid them purely for user experience reasons, because they make it harder for users to read them.
According to John Mueller, Google does not consider uppercase or lowercase URLs to be a ranking factor. However, do note that Google sees web addresses as case-sensitive, so uppercase and lowercase matter when differentiating separate pages.
Should blog URLs include dates?
You should never add dates to your URL unless the content you are publishing is time sensitive. Users who see old dates in the web address may be less likely to click on your website as they may think the content is too old to be relevant. However, Google has said that having dates in your web address will not directly harm your rankings.
Making sure your content is evergreen will help you maintain your high rankings in the long term.
URL bad practices
Understanding what to do is just as important as understanding what NOT to do, so here is a list of some common mistakes for URL design.
Using underscores in URLs
Underscores should not be used to separate words in your URL since they will not be adequately understood by Google’s bots when crawling your site. Instead, you should always use hyphens as word separators, as Google recommends. Hyphens allow Google’s bot to separate words and phrases in the URL to understand the content on the page better.
Hyphens are also easier for humans to read than underscores and, as we have emphasized above, user experience is critical!
How to find URLs with underscores in Sitebulb?
- The first step is to run a standard audit of the entire website while making sure you tick the following:
- SEO
- Page resources
- Performance and mobile friendliness
- International (if you are engaging in international SEO)
- AMP (if your site has AMP pages)
- In the audit overview screen, there will be an option on the left titled all hints. Click on this option.
- You will then be shown all the issues on your site that need to be fixed, including problems with URL structure.
- You can export these issues into an Excel sheet and go over them in any way you like.
Leaving unimportant words in the URL
It is critical to ensure your web address is as short and easily readable as possible, so you should leave unimportant words such as and, the, or, from etc. Users can read the URL just fine without them. These words take up a ton of valuable space that you could use for another keyword or to better describe your page.
Leaving strings of numbers and characters in the URL
We have already stressed the importance of maintaining a simple and short web address. Adding unintelligible numbers and characters goes against this principle. Numbers and letters make it much harder for the user to remember the address or navigate your website.
Keyword stuffing
When designing a URL, it is crucial to add keywords to help with SEO, but this should never compromise the user experience. Keyword stuffing is when you add too many keywords or repeat keywords. This is rarely an effective tactic for SEO. Your address should only include keywords if they help the user.
Designing URLs for robots, not people
Ultimately, most of our tips and guides to building SEO-friendly links will come to this: creating URLs for human convenience. Google wants its users to find genuinely helpful and easy-to-navigate sites, so it only shows sites with a good user experience.
Common URL issues
There are several fairly common but very specific issues web developers face when designing a website’s structure. We have mentioned key issues below:
Optimizing dynamic URLs
Dynamic URLs are automatically generated anytime a user makes a search on your website. Dynamic URLs are not stored anywhere the way URLs for static pages are. You can optimize your search result pages for search engines as long as you are careful to not create duplicate content (the same search page but sorted differently, for example).
To optimize your dynamic page web addresses, shorten them as much as possible by removing unnecessary parameters. You can also use the mod_rewrite module to automatically rewrite them to contain keywords or be more concise.
Designing URLs for pages that allow for sorting and filtering
Most modern search pages allow users to sort and filter results to make it easier for the user to find a certain page. Each sort or filtration option needs to change the dynamic web address slightly since it loads a new page, drastically increasing the number of URLs on your site.
According to Google, this increase in URLs makes Google crawlers’ job significantly more complex since they will have to crawl every single URL that is dynamically created. To avoid this issue, use a robot.txt file and block all or most unessential dynamic URLs. Google advises to not try to get your dynamic pages to rank because it will waste your crawl budget.
Creating URLs for product pages with a lot of variants
Products often come with small variations (for example, different colors, size or material), so it might not make sense to create a separate page for them. In these situations, if you are okay with Google only indexing one version of the product and want to display all variations on the same page, you can just use optional query parameters.
You need to set up these parameters, so a default variation of a product is marked as canonical. This way, Google understands that it only needs to show this one variation in search results. You should mark all other variations with an identifier like ?size=large. This identifier creates alternative pages for each variation, bringing the following benefits:
- Google will show all product variations in their product rich results.
- All product variants will be available on Google Shopping.
Using fragment identifiers (# color or #size, for example) and avoiding creating multiple pages is still an option but this approach renders your products ineligible for the formats mentioned above.
Impact of breadcrumbs on the importance of a URL
Breadcrumbs are a handy tool to help bots and people navigate through your site. It usually consists of a small amount of text on the top of the page that links to the path the user has taken through the site, as seen in the image below.

Breadcrumbs are great for SERPs but even better for user experience.
SEO-friendly links give Google a better idea of how your site is structured. Breadcrumbs could appear in Google search results in place of the web address if you are using the correct structured data. Even though Google may choose to show users the page’s address if the structured data is present, URLs must always be well optimized.
Designing country-specific URLs for local SEO
If you want to rank internationally, then country-specific URLs are likely not for you. However, they can be helpful for local rankings in specific countries. Adding a country-specific domain to the entire site or a particular page can improve your rankings in your chosen country.
This improvement will cost your rankings everywhere else, so you should use this option cautiously. Below are examples of geotargeting:
- Website.ca (This applies to the entire website)
- Ca.website.com (This creates a geotargeted subdomain)
- Website.com/ca/ (This will only apply to a specific page)
You can always geotarget your site via the Search Console’s international targeting report and not change your domain.
If you need a refresher on the different types of domains, sub-domains and subfolders, read our post on domain structuring.
Building URLs for alternative language pages
You should use different slugs for each alternative language version of a specific page. Keeping them distinct ensures that Google crawls each variation of the said page. Just make sure to use the hreflang tag, so Google knows this is just a translation of existing content.
Improve your URL structure and SEO performance
Constructing the perfect URL structure for your website is absolutely critical when it comes to ranking well and improving your click-through rate. Your chosen URL design will likely have an impact on how your entire website is structured so it is important that you follow all of the above guidelines.
If you need help improving your rankings and conversions, reach out to our team of SEO experts who will be happy to guide you to the first page of Google’s search results.
FAQs
How should alternate versions of an existing page be handled?
Alternate versions of a page with separate slugs must be marked as alternates so Google does not penalize your website for duplicated content. The easiest way to do this is to mark one version of the page as canonical, letting Google know that this is the version it should show in search results.
Should session IDs be used in URL structure?
No, you should always avoid temporary parameters such as session IDs since they give your link a certain lifespan. If you have to include these parameters, make sure Google does not index them via your Robot.txt file.
Should your URL contain geotargeted keywords/domains?
Localized words in geotargeted pages will not cause any issues and may improve the site’s user experience. You should be using UTF-8 encoding in your URL to ensure there are no issues with localized keywords.
Here is a localized SEO slug example:
website.mx/el-sito-web
Should non-canonical URLs be in a sitemap?
No, the sitemap should only include URLs you want a search engine to index. If a page is marked as non-canonical, the search engine crawler will be instructed to not index it. This conflicting signal could cause the crawler to disregard your sitemap entirely.
What is a vanity URL?
Vanity URLs are links that have been shortened to be more memorable. They are generally created for branding purposes.
How to change URL structure in WordPress?
In order to change the URL of a WordPress page, open up the editor for that page and go to the right sidebar. Click on the permalink section where you can edit the slug to be whatever you need. This will change the slug of your web address.
If this option is not available, go to settings and then to permalink settings, where you can switch to the post name setting to enable editable slugs.
Do long URLs affect SEO?
URL length is not considered a ranking factor by Google but it can impact SEO in other ways. Since the address is shown in search results, a long or messy slug could reduce your click-through rate, which will reduce your rankings. The maximum length of a web address to be fully shown on the search results page is 200 characters.