It may be intuitive to assume that having not one but multiple pages competing for the desired keyword will only increase your traffic. But that is not the case.
Keyword cannibalization will often reduce your overall traffic and may even hurt your rankings. So let’s define this term and figure out exactly when keyword conflicts pose a search engine optimization (SEO) issue.
What is keyword cannibalization in SEO?
Keyword cannibalization occurs when multiple pages on a website compete for the same intent keyword, causing it to have lower conversions and authority than having a consolidated page.
Since these pages are competing with each other, any SEO boost to one page hurts the other pages (yes, Google will still select the one it thinks is more relevant and define it as canonical). This means you will either have to pick one page to properly optimize or risk diluting your SEO and link-building campaigns across numerous pages, making your efforts less effective.
Cannibalization can hurt most when a low-converting page outranks a high-converting page for a keyword, dropping your overall conversions. Why should users land on a low-converting blog post when they could instead land on a thorough product page with a higher conversion rate? A higher conversion rate means more lead generation, which is usually the goal of enterprise SEO.
Why is keyword cannibalization bad for SEO?
Cannibalization can dilute any search optimization you conduct on your site, particularly if the keyword being cannibalized is essential to your lead generation strategy.
Below are the different ways keyword conflicts can hurt your organic search performance:
Backlinks
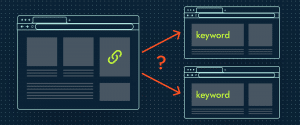
If you have multiple pages focusing on the same concept/keyword, other content creators will not know which page they should be linking to, splitting all of the authority you could be getting from backlinks.
By making sure your pages are highly focused, you can ensure all relevant backlinks are pointing to the page you want them to. This approach also makes link management and building easier.
Content and authority
If Google is showing users multiple pages from your site for the same keyword, these pages must have substantially different content or Google would pick one as canonical. This difference means you have distributed quality content among two different pages instead of consolidating it into one highly useful and detailed page.
Users will likely prefer one consolidated page instead of having to find the information they need on numerous pages. Having a comprehensive piece of content can do wonders for your website’s perceived authority in your chosen niche. Users will be more likely to trust your expertise if they see you publishing helpful and valuable content.
Conversion rates
If a page that has a lower conversion rate is cannibalizing a page that has a higher conversion rate, then all the traffic that the low-converting page attracts is wasted. Traffic is only really useful if it leads to conversions, so if a low conversion rate page is hurting a high conversion rate page, then cannibalization is hurting your website.
How to identify keyword cannibalization?
Now that we understand what keyword cannibalization is and how it can hurt your website, we need to understand how we can remediate it.
There are 2 different ways cannibalization can occur and we will be going over how to find each.
1. More than one page is ranking for a keyword
Having multiple pages ranking for the same keyword simultaneously is relatively easy to recognize. All you have to do is follow these steps:
- Check your site’s rankings for a short period of time in any SEO tool or search console.
- Export that data onto an Excel sheet (or equivalent).
- Check the list of keywords your site is ranking for and look for any duplicates.
- A duplicate keyword in this list means cannibalization is likely occurring but be sure to double-check by Googling the keyword in question.
Once you have found the keyword conflict, check if it’s hurting your site before you move to fix it. It may not be worth redirecting a page if it is on the 10th page of Google for a keyword you are already ranking well for.
2. Multiple pages are taking turns in ranking for the same keyword
When multiple pages start taking turns ranking for the same keyword, users will have an inconsistent experience with your website and may end up landing on low-converting pages. Identifying this issue is a little tricky since it is unlikely you will spot it in a routine rankings check, particularly if you have a large website.
If you want to find this kind of cannibalization, check your site’s rankings over a longer period of time, such as 3 months. Then look for duplicate keywords by using the same method detailed above. Once you find an instance of cannibalization, make changes only to the page that has a lower conversion rate. If the conversion rates are the same for both pages, then adjust the page that has worse rankings.
What tools can you use to find keyword cannibalization?
Some SEO tools allow you to check for cannibalization without exporting any data. We will be discussing the most common SEO software below.
Google Search Console
One of the most essential SEO tools in your arsenal, Google Search Console (GSC) will help you identify most search-related issues on your website, including cannibalization.
Go to your search results view and set a particular timeframe:
- If you are looking for cannibalization where two pages rank for the same keyword simultaneously, pick a smaller timeframe (under a month).
- If you are looking for cannibalization where two pages are flip-flopping for the same keyword, then it is best to check on a longer timeframe (around 3 months).
Next, all you have to do is either export your ranking data to a sheet or investigate particular keywords within the tool. If you already know what keywords to check for, then you can filter all of the data to only show you rankings for that particular keyword. Once filtered, you can view the pages tab to see what pages are ranking for that keyword, as shown below:

The Search Console is an invaluable tool for monitoring your search performance.
Moz
If you have a fully set up and paid account for Moz, you can use the Keywords Explorer tool to check for keyword cannibalization.
First, type in your website’s domain as well as the location of your audience, then look through all the keywords your site is ranking for. Each keyword will have a drop-down menu showing you other positions your site may have for the same keyword. This drop-down will reveal any cannibalization occurring on your site.

Moz will only be useful for this task if you have a paid account.
This method is a little slow and tedious. If you want to run a full site audit, you may be better off exporting all your ranking data to Excel. Depending on the kind of cannibalization you are looking for (we recommend you check for both), you should use one of the methods discussed above.
Semrush
Semrush actually has a separate view that will show you any cannibalization issues occurring on your site. This view will only be available if you opt for the Guru or Business plans and is located within the position tracking tool. This view will show you any keywords that have multiple URLs from your site ranking for it.

Semrush allows for very quick cannibalization audits with this tool.
Ahrefs
Ahrefs also has specific functionality to help you track cannibalization. All you have to do is look at your organic keywords in the site explorer tool. You can filter the results only to show you keywords that have multiple URLs from your site ranking for them.
This method will not spot cannibalization where multiple pages are alternating for the same keyword. For that situation, you will just have to look through your historical rankings and look for duplicate keywords.
Can keyword cannibalization be good?
Keyword cannibalization can harm your organic search performance, but it does not mean it is always bad. Sometimes cannibalization will not be worth dealing with or may even be helpful for your site.
Keyword conflicts should only be dealt with if they are hurting your rankings in a significant way.
If two of your pages are ranking for the same keyword, but one page has the top position while the other one is on page 10 of Google Search, then both pages are ranking for multiple keywords. In this case, it will not be worth it to solve the cannibalization issue since removing one of the pages will cause a large decrease in traffic. If both pages rank for many different keywords, you will need to take traffic from those keywords into account.
Cannibalization can also be helpful for a site in a few cases. If two high-converting pages rank in the top 10 for the same keyword, particularly in the top 3, you should just leave those pages as they are. Gaining more real estate on the search results page is a surefire way to increase your click-through rate (both pages combined) and visibility.
Google does recommend that you only create one strong page for a particular keyword/user intent instead of multiple weaker pages. So it is not recommended that you actively try to get two different pages to rank for the same keyword, but if it happens to occur on its own, you don’t always need to fix it.
How to fix keyword cannibalization?
There are many different solutions to keyword cannibalization depending on the kind of cannibalization you are experiencing. Here are the most effective solutions:
301 redirects
The surefire way to fix cannibalization is to set up 301 redirects from the offending page to the page that should be ranking. A redirect will impact the correct page positively as it will transfer all ranking signals from the cannibalizing page over to the correct page. This method will remove the cannibalizing page from your website.
Canonicals
If you have multiple pages with similar content that are ranking for the same keyword and you cannot delete any of them, then you should be using canonicals. A canonical tag is a special HTML tag that lets Google know what page it should show in its search results. All pages with similar or duplicate content should have a canonical tag that points to the page you want Google to show in its search results.
Below is an example of a canonical tag:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://productiveshop.com/demand-generation-leaders//” />
No-indexing
There will be cases where you cannot delete a page because it is important to your site. In this case, it will be easiest just to no-index the page. This way, Google will not index it and won’t appear in any search results. Do note that this method should only be used if you are comfortable with the no-indexed page not getting any search traffic at all.
Checklist for identifying and solving SEO page conflicts
- Identify your keyword cluster (and the critical keywords within it).
- In Google Search Console, filter by those keywords to see which pages are harvesting the keywords.
- Note that it’s okay for the same keyword to be harvested on multiple pages. It’s inevitable. However, the goal is that the keyword should not be the primary intent focus of that page.
- Understand the context of the pages and identify which of them is more geared toward satisfying your prospect’s intent.
- Understand which of these pages are attracting the most healthy traffic.
- Identify the position these pages are holding in SERPs.
- Run a quick keyword gap analysis between similar pages to ensure you don’t leave critical keywords behind (on the page you are about to redirect from).
- Adjust the most important page to include content that was on the cannibalizing page to close the keyword gap.
- Decide whether or not to use 301 redirects
- Do not delete (from your CMS) the page you decided to redirect.
- Continuously monitor the impact you’ve caused (to understand if you need to revert or not).
How to prevent keyword cannibalization?
The best way to avoid keyword cannibalization is to optimize your pages for particular audience searcher intent. It helps to understand your buyer persona challenges first. In other words, you should not only optimize for specific keywords but also ensure that your pages answer particular questions that users are asking.
Keywords like “what is software as a service” and “software as a service definition” target the same user intent. These users want to understand software as a service.
If all of your pages deal with specific user intent and none overlap in content, then you shouldn’t encounter keyword cannibalization. Try to make sure there is as little overlap in content as possible.
Create a comprehensive SEO strategy
Creating a detailed SEO strategy for your website is essential to succeed in organic search but can be difficult to create. Get in touch with our team of value-driven experts for help.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to spot cannibalized keywords?
To spot a cannibalized keyword, just export your ranking data from Google Search Console or a tool like Semrush’s position tracker, then follow these steps:
- Look at data that shows the keywords your site is ranking for as well as the pages that are ranking.
- Sort this data by keyword.
- Find all keywords that are appearing more than once. Having duplicate keywords means that more than one page from your site is ranking for that keyword.
What do I do when there are two pages with similar content?
Two pages having similar — not duplicate — content is not necessarily a problem and will not always lead to cannibalization. So long as these pages are answering distinct questions and dealing with specific user intent, you should not encounter any keyword conflict issues.
For example, our article on homepage meta descriptions and our detailed guide to metadata are both similar but deal with different searcher intents. One is specifically about meta descriptions for homepages while the other is a generalized metadata guide.
Similar content could still hurt your website as similar/duplicate pages now impact the entire website’s rankings negatively due to Google’s helpful content update. So try and make all of your pages as distinct as possible. If both pages are important for the website and answer the same user intent, then consider making one of the two pages canonical.
Were indented rich results created to fix keyword cannibalization?
Indented rich results appear when a domain has multiple pages that could be relevant to a particular search query. Although indented results can alleviate some instances of cannibalization, they will not always solve the problem since there is no guarantee that they will appear.

Indented results can give you a lot more space on the search results page.
It is best not to pin your hopes on getting indented rich results. If you chase after them, you may just end up cannibalizing your own content.
Will Google’s new helpful content algorithmic updates have a severe impact on pages targeting the same search intent?
No. The helpful content update will not target pages that target the same searcher intent. It will instead penalize thin or duplicate pages. Google’s goal with this update is to crack down on content that is not helpful for users, so as long as your page provides value that is not provided anywhere else on your site, you should be fine.
Interested in crafting helpful content? Start with our thin content guide.