Remember the days when websites got away with keyword stuffing and cloaking? Neither do I. But believe it or not, there was once such a time.
In those days, some marketers and business owners would paste content from other websites and build shady backlinks to get their pages to rank highly on search engine results pages (SERP). These tactics successfully resulted in the plagiarized pages exceeding the original content owners’ rankings.
Enter the Google Panda algorithm update (named after the engineer who came up with the breakthrough). On February 23, 2011, many webmasters woke up to website rankings taking a huge dip. The Panda algorithm’s objective was to end the high SERP rankings of low-quality websites and the rise of “content farm” business models. Content farms are websites that produce large amounts of low-quality content to satisfy algorithms and rank for as many keywords on SERP. In 2013, Google took a step further, stating that thin content was against its Webmasters Guidelines and introducing a manual thin content penalty.

What is thin content?
Thin content is content that provides little or no value to its audience. In other words, content that is not fulfilling and leaves you hungry for more.
Types of thin content that impact SEO
Content that lacks depth

Most pages on your website must target a keyword and satisfy a user’s intent while covering the topic with helpful information. If the web pages lack depth, search engines might label your content as thin, and your users will bounce off.
Duplicate content
While it’s a given that content should never be copied word for word, sometimes duplicate content can occur due to technical issues. For example, HTTP URLs that have not been redirected to their HTTPS counterparts or similar pages that have not been canonicalized may appear duplicated.
Scraped content

Content taken from other sources and reputable sites that is not original is considered thin—especially if no additional context is added to your website to give more value. This might also account for copyright infringement. Creating unique content will lead to better results in the long run and will ensure repeat visitors.
Doorway pages

Doorway pages are pages built to rank for similar search queries. For example, pages are generated to funnel visitors into an actual converting page on the website. They present an awful user experience by redirecting users to less valuable or affiliate pages.
Affiliate pages

Webpages with numerous affiliate links that add little or no value to users are considered thin content for SEO. To ensure that affiliate pages are not penalized, include links that match your target audience.
Automatically generated content
Automatically generated content such as automatic transcriptions and translations are considered thin as they are a byproduct of automated sources that a human has not reviewed. AI content is on the rise, but AI content with no human review or curation will likely not get you the results you need.
☝️ Learn how to automate content creation without compromising quality.
Content with poor spelling and grammar

With tools like Grammarly, there is no excuse for having poor grammar, punctuation issues or spelling errors on your websites. Untidy pages hurt your credibility and signal to readers that you did not take the time or effort to review the copy for mistakes.
Why thin content hurts SEO
Thin content hurts SEO because it’s often associated with:
Keyword cannibalization
Keyword cannibalization occurs when you have multiple identical web pages spread through your website competing for the same keywords. Pages competing for the same keywords can confuse search engines, as it becomes unclear which content should rank higher. As a result, your rankings are greatly diluted, which may cause a lower priority webpage to rank higher than the other.
High bounce rates
Usually, an increase in metrics is not alarming—except when it comes to bounce rates. Although bounce rates are not a direct SEO ranking factor, they can hurt your conversions. Users will not waste their time on low-quality and shallow pages and will go back to find search engine results that answer their queries better.
Absence of backlinks
It’s always a win when other websites link back to your page. Backlinking is almost always exclusive to web pages with great content. Thin content reduces your chances of getting backlinks, and it will also almost always brand your website as untrustworthy.
How to identify thin SEO content
There is no right or easy way to identify thin SEO content since we don’t have access to Google’s algorithm. However, there are indicators and warning signs that can trigger an investigation into a web page’s content. Below are some of the tools and methods to use:
Read your content
This suggestion might seem like a no-brainer, but surprisingly, many people don’t know what content exists on their website. Manually going through content to ensure quality is up-to-par is a tedious yet necessary step of your thin content audit.
Use website crawlers and other tools
There are excellent SEO crawlers on the market that can help you locate thin content on your website.
Screaming Frog
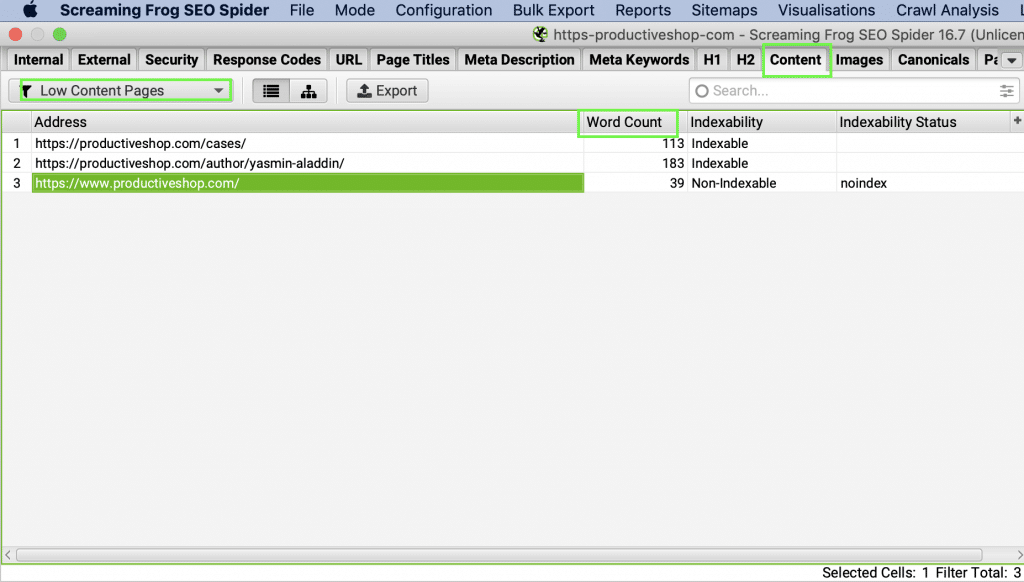
Here, I am using Screaming Frog as a thin content crawler. Download the trial version and start by crawling the website.
Next, go to the Content tab and select:
1. Low content pages
Screaming Frog will indicate which pages have a low word count. It’s worth mentioning that a low word count in itself does not automatically label a page as thin because some pages warrant a fewer number of words. However, a manual check on these pages will enable you to make a decision.
2. Exact Duplicates
The pages with exact duplicate content will populate.
3. Near duplicates
The pages with near duplicate content will populate.
4. Spelling/grammar errors
The pages with spelling and grammar issues will populate.
5. Duplicate meta titles
The pages with duplicate meta titles will populate.
Copyscape
Copyscape is another thin content checker tool that can be used to check individual pages for plagiarism and duplicate content. The premium version enables users to scan an entire website. It’s worth mentioning that in some cases someone might have copied original content from your website to theirs, which will still hurt your rankings.
Grammarly
Grammarly is a great affordable tool for checking all your content’s grammar, spelling and readability. Grammarly also offers a plagiarism checker, which will ensure your content is unique to avoid getting penalized by search engines.
How to fix thin content on your site
Here are some steps that you can take to ensure your content is high quality:
Beef up thin content
Optimize existing posts for search engine optimization (SEO). You can optimize your page by focusing on a select number of keywords and rewriting the page accordingly. Aim to answer the searcher’s question and fully cover the topic. Also, don’t forget to include videos, images or media as they greatly enhance the user experience.
Repurpose or combine content
Sometimes we have valuable and informative content but the concepts are covered over multiple pages or blogs. Repurposing content over several pages causes keyword cannibalization and will ultimately dilute your rankings on search engines. The solution is simple: fortify one vital piece of content using the information from the fragmented posts.
Delete thin content
When all else fails, go ahead and delete content—no matter how much it might hurt. You should eliminate outdated content, posts targeting irrelevant keywords or posts that are off-brand and off-topic. In the long run, you will avoid getting penalized and more importantly, you will provide your users with a better user experience and relevant content of higher quality and value.
Fix technical issues
Sometimes the issue is not with the content itself but rather technical issues that give search engines thin content indications.
Here are common technical issues that contribute to thin content and signal to Google that there are two different pages of the same content.
- HTTP vs. HTTPS: Ensure all HTTP links are redirected to the HTTPS version.
- www vs non-www URLs: Choose one preferred URL and ensure the other version is redirected to the desired URL.
- Comment pagination: Content management systems (CMS) like WordPress enable an option to allow comment pagination. This leads to the creation of new URLs for each individual page of comments. The solution is to either deactivate this option from the CMS or canonical the pagination series.
- International SEO lacking geo-targeting: This occurs when similar content pages exist on a website targeting different locations. For example, US and UK. The solution is to use hreflang tags for language and region URLs.
Pro tip
Before making any decisions regarding scraping or combining content, it is crucial to quickly check if any pages in question have backlinks built back to them. This will enable you to make the following decisions:
- If backlinks are built, the content may not be as thin as you might have thought and you just need to optimize it further.
- If the content is off-brand and you still want to delete it, redirect it to the most relevant page on the website to maintain any SEO juice received from the backlinks.
- If you consider combining content into one page, the number of backlinks built to the pages will allow you to choose which URL you will keep and which you will redirect.
- Ensure that your copy is free from grammatical and spelling errors that can hurt your SEO results. Check our guide on how to make your content shine [checklist included].
Summary: High-quality SEO content is key to improved user experience
The bottom line is Google values user experience above everything else and thin content harms the user experience. When search engine result pages (SERP) are populated by high-ranking content that lacks value, contains spam or causes frustration, users will use another search engine and bounce right off.
So, keep the search giant happy by keeping the users happy with original content that satisfies their intent, adds value and answers their queries.
Once you have cleaned up your content, make sure that you maintain your progress and build a killer editorial calendar. If you need further help with B2B thought leadership, reach out to our editorial team for support.