Drupal is an enterprise-grade content management system (CMS) powering some of the world’s leading B2B tech companies. This glossary helps marketing leaders understand how Drupal’s features align with typical B2B tech needs, from complex content workflows to secure integration capabilities.
Need to build a Drupal site or get support? See our Drupal services page.
Who this guide is for:
- Chief marketing officers
- Marketing directors
- Demand generation managers
- Heads of content
What makes this CMS different? What is Drupal used for?
Unlike simpler CMS platforms, Drupal is built for complex content operations that B2B tech companies require.
So what is Drupal CMS used for?
The platform excels at handling:
- Multiple content workflows
- Complex user permissions
- API integrations
- Secure data handling
- Scalable content operations
Example: A cybersecurity firm uses Drupal as its CMS to manage different content access levels — public blog posts, gated technical whitepapers, partner-only documentation and customer-specific security advisories, all from a single platform.
Is Drupal a good CMS? What are the benefits?
Drupal CMS empowers businesses with flexibility, scalability and seamless integrations, making it a powerful choice for enterprises looking to future-proof their digital platforms. Let’s review the Drupal benefits:
Enterprise scalability
The Drupal platform handles growth in content, users and traffic without rebuilding your infrastructure.
Drupal use case: A fintech platform scaling from:
- 100 to 10,000 pages of documentation
- 5 to 50 integrated product APIs
- Single to multi-language support
- Basic to complex compliance requirements — all without changing platforms
Integration capabilities
Drupal’s API-first architecture connects with your B2B tech stack.
Drupal use case: A sales software company that integrates Drupal with:
- Salesforce for lead tracking
- Marketo for marketing automation
- Zendesk for support tickets
- Custom pricing calculators
- Product documentation systems
Content workflow and governance
The Drupal software supports complex approval processes and content governance requirements.
Drupal use case: A document sharing system’s workflow in which:
- Technical writers draft content
- Product teams review technical accuracy
- Legal reviews compliance
- Marketing optimizes SEO
- Regional teams handle localization
- Product owners give final approval
- There’s automated content publishing based on the release schedule
Drupal architecture and features: What are the core building blocks?
Drupal is built on a modular architecture that allows flexibility and customization. Its core building blocks provide the foundation for managing content, users and functionality efficiently.
Understanding the Drupal architecture and features is key to leveraging the plaform’s full potential.
Nodes
Node in Drupal represents the fundamental content unit. Beyond basic content, nodes support versioning, allowing you to track changes and revert to previous versions. They also have a publishing workflow with states like published, unpublished and archived. Each node automatically gets a unique URL and can be referenced by other content.
Scenario: A news organization uses nodes for their articles, where each article goes through multiple revisions. Editors can track changes through version history, seeing who modified what and when. When a controversial article needs updating, they can easily compare versions and roll back if needed. The automatic URL generation creates SEO-friendly paths like “/news/2024/breaking-story-title.”
Content types
Content types are powerful templates that shape how content is structured. They’re fully customizable with their own workflows, permissions and display settings. For example, a “Product” content type might include price fields, inventory tracking and image galleries, while an “Event” type could have date fields, location maps and registration forms. Content types can also have their own URL patterns and custom submission forms.
Scenario: A university builds different content types for their website:
- “Course” type with fields for credits, prerequisites and professor assignments
- “Faculty Profile” type with academic history, publications and office hours
- “Research Project” type with funding details, team members and project timeline
Each type has its own structured data and approval workflow involving department heads.
Fields
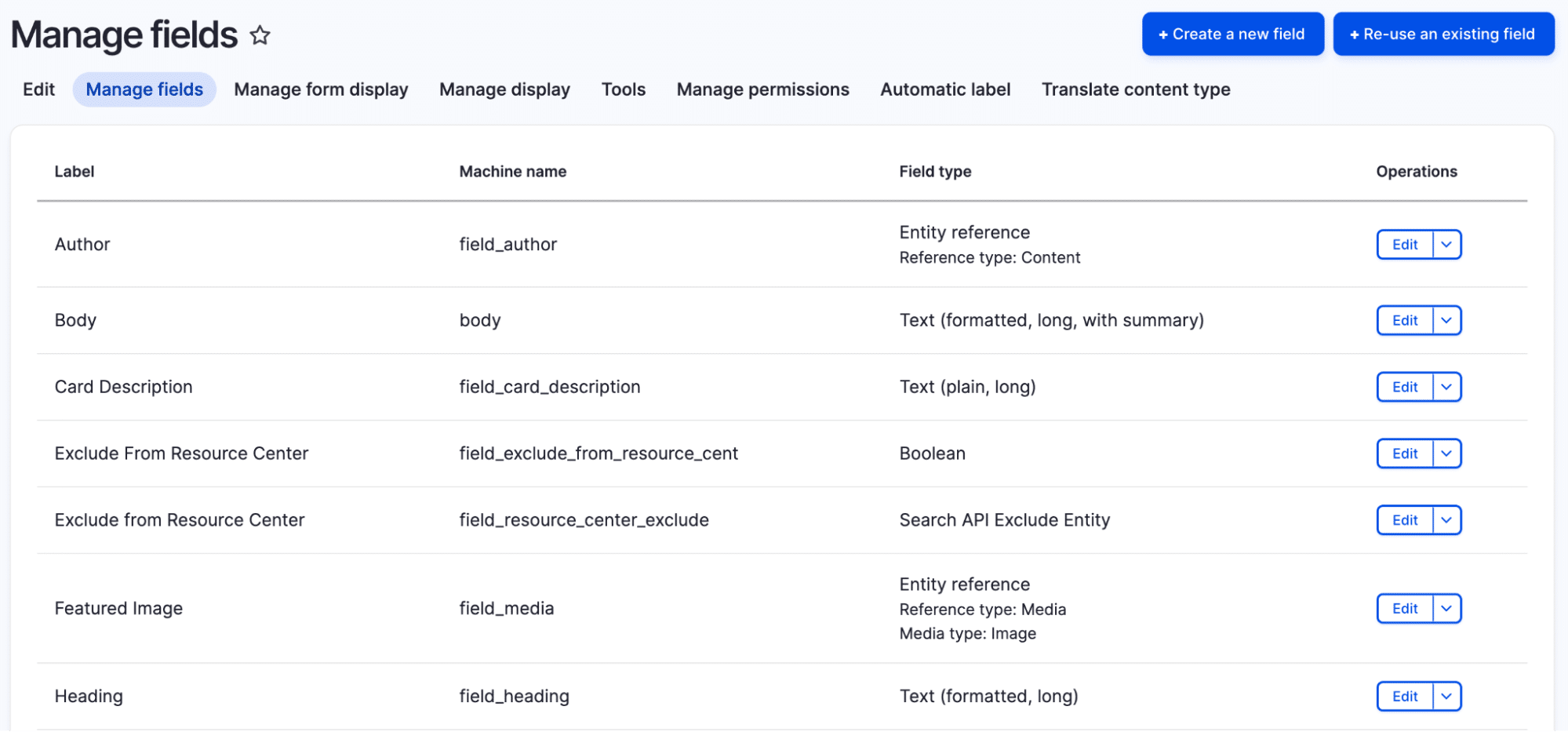
Fields make Drupal extremely flexible. Beyond basic types like text and numbers, fields can handle complex data like geolocation, media libraries and entity references. Each field can have its own display settings for different contexts (full page vs. teaser), validation rules and default values.
Fields can also be conditional, appearing only when certain conditions are met.
Scenario: A learning management system’s “Course” content type includes fields for:
- Course title
- Learning objectives (structured list)
- Prerequisite courses (reference field)
- Certification requirements
- Integration APIs
- Compliance requirements
Views
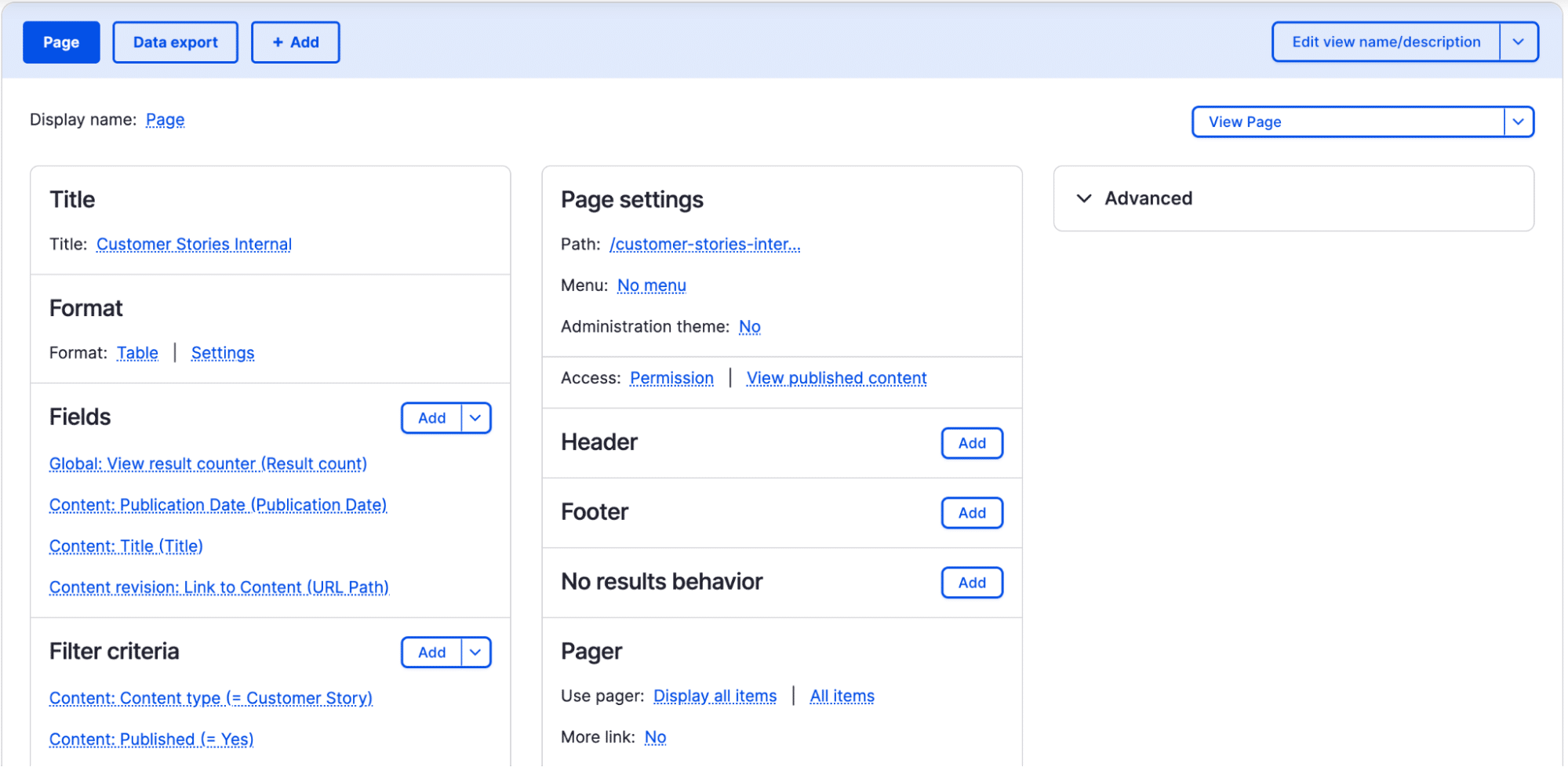
Views are one the most powerful Dupal features — creating dynamic content displays like calendars, maps or slideshows. Views support contextual filters (changing content based on URL parameters), relationships (connecting different types of content) and aggregation (grouping and summarizing data). They can also generate RSS feeds, JSON endpoints or CSV exports.
Scenario: A sales software company uses Views to create:
- ROI calculator results
- Feature comparison matrices
- Integration ecosystem directory
- Customer success stories filtered by industry
- Marketing resource center with faceted search
Taxonomies
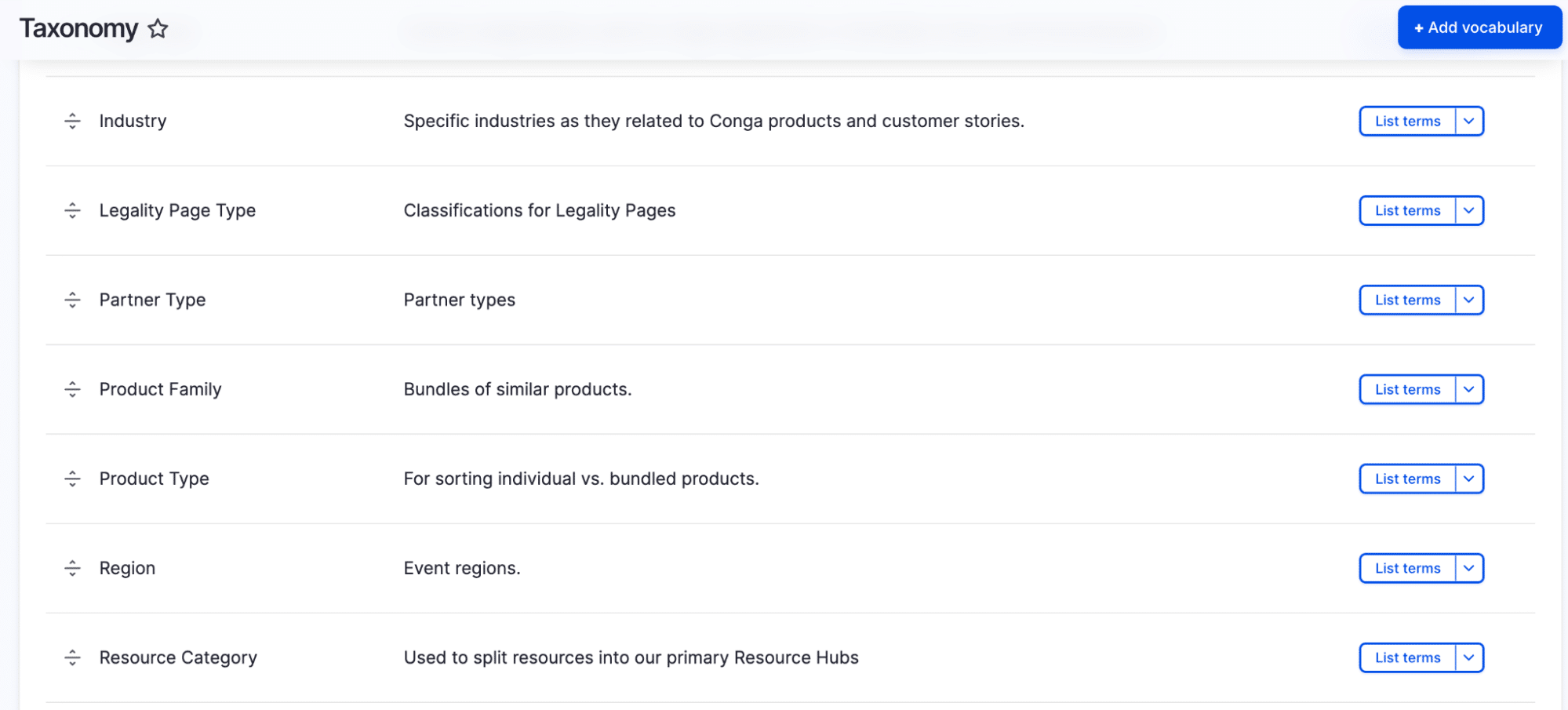
Taxonomies provide sophisticated content organization. They support both flat and hierarchical structures, with terms that can have their own fields and relationships. You can create multiple vocabularies for different purposes — like product categories, content tags or geographical locations. Terms can be automatically generated from the content or managed manually.
Scenario: A recipe website implements multiple vocabularies:
- “Cuisine Types” (hierarchical): Asian > Chinese > Sichuan
- “Dietary Requirements” (flat): Vegan, Gluten-Free, Keto
- “Cooking Time”: Quick (30min), Medium (1hr), Long (2hr+)
- “Difficulty Level”: Beginner, Intermediate, Advanced
These taxonomies power their advanced recipe search and filtering system.
Blocks
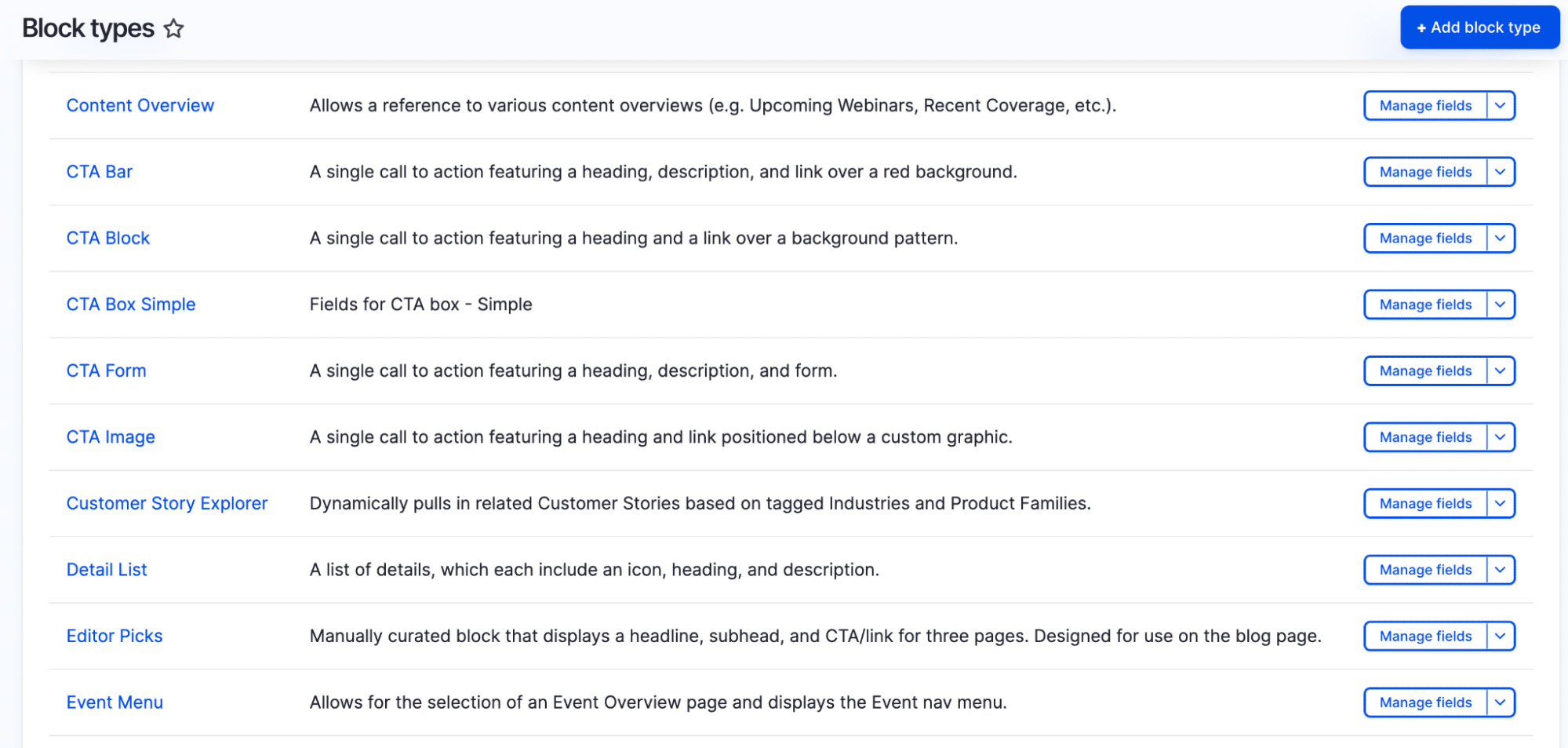
Blocks are versatile content containers. They can be configured to appear on specific pages, for specific user roles or during certain time periods. Blocks can contain static content, dynamic Views output or custom PHP code. They’re essential for creating responsive layouts and can be placed using Drupal’s layout builder.
Scenario: A retail chain’s website uses blocks for:
- Store locator in the sidebar that detects user location
- Holiday promotion banner that appears only during sales periods
- Social media feed in the footer
- Customer service chat widget that appears based on user behavior
- Emergency notifications that administrators can toggle
Themes
Themes control the entire visual experience. They can include mobile-first responsive designs, custom color schemes and typography settings. Themes use template files (Twig in Drupal 8+) to override default markup and can provide theme settings for site administrators to customize appearances without coding.
Scenario: A restaurant chain implements a theme with:
- Different color schemes for each location
- Custom typography matching their brand guidelines
- Mobile-first design that transforms the menu into a touch-friendly format
- Special layouts for event pages and catering information
- Print stylesheets for downloadable menus
Modules
Modules extend the platform’s capabilities.
- Drupal core modules provide essential functions like path aliasing, content moderation and media handling.
- Contributed modules can add features like e-commerce (Commerce), page building (Paragraphs) or search enhancement (Search API).
- Custom modules can integrate with external systems or implement site-specific functionality.
Scenario: A non-profit organization extends the capabilities of their website with:
- Donation module for handling contributions
- Event registration module for volunteer sign-ups
- Social media integration for campaign sharing
- Newsletter module for donor communications
- Custom module tracking volunteer hours and impact
Entities
Entities are Drupal’s base data structures. While nodes handle content, other entity types manage different aspects of the site. For example:
- Media entities handle reusable media assets
- Taxonomy term entities manage categorization
- Custom entities can handle specialized data like product reviews or event registrations
Scenario: A museum creates custom entities for:
- Artwork pieces with detailed provenance tracking
- Exhibition planning with room layouts
- Conservation records linking to artworks
- Visitor feedback collection
- Audio guide content management
Regions
Regions define the structure of your pages. They work with the theme system to create responsive layouts. Each region can have its own styling and behavior, and regions can be conditionally displayed based on content type, user role or other factors.
Scenario: A fashion blog structures its theme with regions for:
- Trending stories ticker at the top
- Instagram feed in the right sidebar
- Newsletter signup in the footer
- Shopping recommendations below articles
- Seasonal campaign banners between content sections
Menus
Menus enable site navigation, supporting the hierarchical organization of your site. Menu items can have their own attributes and be translated for multilingual sites. Drupal also supports special menu types like breadcrumbs and tabs.
Scenario: An educational platform organizes content with:
- Course catalog menu that updates automatically
- Student dashboard navigation based on enrolled courses
- Faculty administration menu visible only to instructors
- Resource library menu with nested categories
- Progress tracking breadcrumbs
Users and roles
Users and roles provide granular access control. Users can have multiple roles, each with specific permissions. Roles can be used to control access to content creation, editing and administration features. Drupal also supports single sign-on solutions and complex authentication scenarios.
Scenario: A media company sets up roles for:
- Writers who can create but not publish content
- Editors who can review and publish
- Ad managers who control promotional content
- Subscribers who access premium content
- Administrators who manage site configuration
Configuration management
Configuration management enables reliable deployment between environments. It tracks changes to site structure, views, fields and other settings. Configuration can be exported to code, version controlled and synchronized between development, staging and production environments.
Scenario: A web development agency manages multiple client sites by:
- Developing new features in local environments
- Testing configurations in staging
- Using version control for configuration changes
- Deploying tested configurations to production
- Maintaining different configuration sets for each client
Get an in-depth understanding of Drupal’s fundamentals
Preparing for Drupal implementation
Before starting Drupal development, dedicate time to learning about Drupal’s structure and basic functionality. This will help you understand what you’re getting out of the box and what will likely require additional development. You will also need to find a good Drupal developer (or, you know, just shout us a message!). Learning as you go doesn’t work well with Drupal software due to its complexity.
Resource planning
Here’s a breakdown of typical resource requirements for B2B tech companies.
| Role in the Drupal project | Responsible for |
|---|---|
| Digital marketing manager (platform owner) |
|
| Content strategist |
|
| Developer |
|
If you need a major update for your website, you can outsource work to an agency partner. In addition to your existing team, you’ll have access to:
| Role in the Drupal project | Responsible for |
|---|---|
| Project manager |
|
| Designer |
|
| Content writers |
|
| Developers |
|
| QA |
|
| SEO specialist |
|
The technical prerequisites for devs
Timeline considerations
Setting realistic timelines is crucial for successful project execution. The timeframe can vary depending on the complexity and scale of the project.
For example, an enterprise B2B tech implementation may require:
- Discovery and planning: 4-6 weeks
- Design and architecture: 6-8 weeks
- Development: 12-16 weeks
- Copywriting: 4-6 weeks
- Content migration: 4-5 weeks
- Testing and training: 4 weeks
- Client review and adjustments: 2-4 weeks
- Launch preparation: 2 weeks
- Post go-live fixes: 2 weeks
Keep learning:
How to set up a Drupal site: Step-by-style guide for enterprises
Cost of Drupal CMS implementation vs other CMS platforms
| Phase | Drupal | WordPress | Webflow |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial build |
|
|
|
| Maintenance |
|
|
|
| Example | Enterprise B2B platform initial investment is higher but maintains complex features without increasing costs | The marketing team needs direct control over a lightweight site for maximum SEO performance and template flexibility | The marketing team can make visual changes but needs a developer for custom features |
A comparison table of Drupal vs WordPress vs Webflow
| Feature | Drupal | WordPress | WebFlow |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise security | Enterprise-grade security with built-in features for complex authorization, API security and compliance requirements — plus, regular security updates from a dedicated team | Basic security features available through plugins; frequent target of attacks due to popularity | Basic security features; limited enterprise security options |
| Content workflow | Complex, customizable workflows with multiple stages, roles and approvals; support to enterprise content operations | Basic draft/publish workflow — with the need for plugins for advanced workflows | Basic publishing workflow and limited workflow customization |
| User permissions | Granular permissions down to field level; custom role creation; complex access rules | Basic role management; additional permissions through plugins | Basic user roles with limited customization |
| API integration | API-first architecture built-in REST API; JSON:API support; GraphQL integration | REST API available; a need for plugins for advanced integrations | Limited API capabilities with basic REST API available on Business/Enterprise plans |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; able to handle millions of pages and concurrent users; multi-site capabilities | Moderate scalability and susceptible to performance issues with high content volume | Good for smaller sites due to limited scalability for large content operations |
| Customization | Highly customizable at every level — with custom content types, fields, displays and functionality | Customizable through themes and plugins; less flexible core functionality | Excellent visual customization; limited backend customization |
| Development cost | Higher initial development cost; lower long-term maintenance costs for complex sites | Lower initial cost but can become costly with many premium plugins | Medium initial cost; ongoing subscription costs |
| Technical expertise | Requires significant technical expertise or agency partner due to steep learning curve | Moderate learning curve; thousands of developers available | Lower technical barrier; focus on visual design skills |
| Content structure | Highly structured content model; custom fields and relationships; content reuse | Basic content structure; additional structure through plugins | Basic content structure; limited content relationships |
| Multi-site management | Built-in multi-site capabilities; shared code base and resources | Multi-site through network feature; limited shared resources | Separate sites require separate accounts/management |
| Compliance support | Strong compliance features for GDPR, HIPAA etc.; audit trails available | Basic compliance features with need for additional plugins | Basic compliance features and limited audit capabilities |
| SEO capabilities | Advanced SEO tools built-in; custom metadata fields; XML sitemaps | Strong SEO through popular plugins like Yoast | Basic SEO features and limited advanced optimization |
| Page speed | Excellent performance with proper configuration; built-in caching | Good performance but requires optimization plugins | Good performance for simple sites, but can slow down with complexity |
| Integration with marketing tools | Enterprise marketing tool integration; custom integration development | Wide range of marketing tool plugins available | Limited marketing tool integrations |
| Database architecture | Flexible database architecture; custom entity types; complex queries | Fixed database structure; limited customization options | No direct database access; limited data relationships |
Keep learning:
Explore our other CMS comparison guides:
Build or maintain your Drupal website with Productive Shop
Whether you’re rebuilding your web presence or need support for your existing Drupal site, Productive Shop has got you covered. Our team of Drupal CMS pros offers a full suite of services to help you get the most out of this powerful platform:
- We understand the complexities of the Drupal software and are equipped to handle everything from web development to ongoing maintenance and search optimization — saving you time and giving you peace of mind that your website is secure, up-to-date and performing at its best.
- We also offer web design and writing services to ensure your site is visually appealing and effectively communicates your message.
Contact us today to discuss your Drupal needs and discover how we can help you convert your website into a lead generation machine.